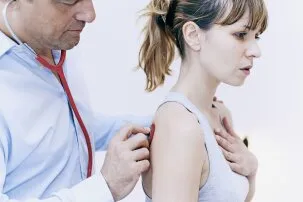
A respiratory therapist is a healthcare professional who specializes in the assessment, treatment, and care of patients with breathing and cardiopulmonary disorders. They work closely with physicians and other healthcare providers to develop and implement treatment plans for patients with conditions such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), emphysema, pneumonia, and respiratory distress syndrome.
Respiratory therapists perform a variety of diagnostic tests to evaluate a patient's lung function, including measuring lung capacity, conducting arterial blood gas analysis, and performing pulmonary function tests. They also administer treatments such as oxygen therapy, aerosol medications, and mechanical ventilation to help patients breathe more easily.
In addition to providing direct patient care, respiratory therapists also educate patients and their families about their conditions and how to manage them effectively. They may also provide counseling and support to help patients quit smoking or make other lifestyle changes to improve their respiratory health.
Respiratory therapists work in a variety of settings, including hospitals, nursing homes, home healthcare agencies, and outpatient clinics. They may also provide care in emergency situations, such as during a cardiac arrest or trauma.
To become a respiratory therapist, individuals typically complete a two-year associate's degree program or a four-year bachelor's degree program in respiratory therapy. They must also obtain a state license to practice, which usually involves passing a national certification exam.
Overall, respiratory therapists play a crucial role in improving the quality of life for patients with breathing difficulties, and their expertise is essential in the diagnosis and treatment of respiratory conditions. Their compassionate care and commitment to helping patients breathe easier make them a valuable asset to the healthcare team.